state相关内容请查看Vuex起步
一、Getters
1.介绍
有时候我们需要从 store 中的 state 中派生出一些状态(对state中的变量进行一些操作或者说是建立函数),并且将这函数应用到多个组件时,如果通过复制函数,或者抽取到一个共享函数然后在多处导入它,这样的代码不够理想。所以就需要用到getters
getters类似于组件中的computed(计算属性),当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算
2.使用
getters中的函数有两个参数第一个是state,第二个是metters。

在组件中展示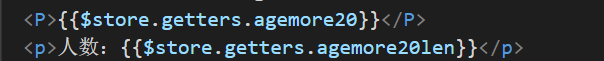
如何向getters里的函数传递其他的参数?
将函数返回值改为函数即可
1 | agefilter(state) { |
1 | <p>{{$store.getters.agefilter(30)}}</p> |
二、Mutations
1.携带额外参数(payload)
在之前提到过如何使用提交mutation修改store状态,那么如何在更新数据时,如何传递一些额外的数据?
在组件中通过commit mutation给store
接收传递过来的参数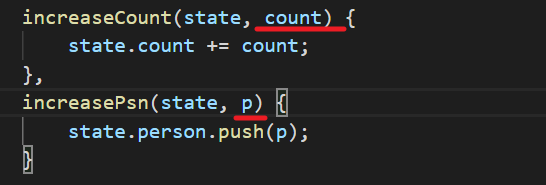
2.两种提交风格
(1)普通方式的提交
1 | this.$store.commit('increaseCount',count); |
(2)对象风格的提交方式
1 | this.$store.commit({ |
对象风格的提交与(1)不同的是,最后接收的count是一个对象
1 | increaseCount(state, count) { |
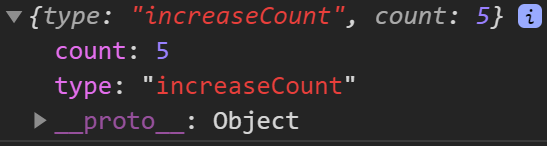
3.Mutation 需遵守 Vue 的响应规则
Vuex 的 store 中的状态是响应式的,那么当我们变更状态时,监视状态的 Vue 组件也会自动更新。这也意味着 Vuex 中的 mutation 也需要与使用 Vue 一样遵守一些注意事项:
- 最好提前在你的 store 中初始化好所有所需属性。
这些初始化的属性都会被加入到响应式系统中,而这些响应式系统会监听属性的变化,当属性发生改变时,会通知所有界面中用到该属性的地方,让界面发生更新 - 当需要在对象上添加新属性时,现在的版本直接添加也能做到响应式,但是官网更推荐这样做:
1 | Vue.set(obj, 'newProp', 123) |
或者,用新对象替换老对象
1 | state.obj = { ...state.obj, newProp: 123 } |
如果要删除某个属性:
1 | Vue.delete(state.obj,prop); |
三、Actions
1.介绍
ction 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
也就是说,当某些情况下确实需要Vuex进行一些异步操作(网络请求……),就需要Action代替Mutation进行异步操作
2.使用
实现在点击修改名称按钮开始的1秒后,将名字修改为WRM:
组件dispatch到action
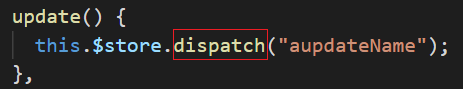
由action执行完异步操作后,再由action提交mutation

mutation
1 | mutations: { |
四、Modules
1.介绍
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割
2.使用
1 | const moduleA = { |
(1)模块内的state
模块内的state会添加到store中的state,所以获取模块内的state属性:store.state.a.prop
(2)模块内的mutations
接收的第一个参数是模块的局部状态对象。调用和之前的store中的mutations一样
1 | const modulesA = { |
1 | modiName() { |
(3)模块内的getters
接收的前两个参数是分别是模块的局部状态对象,局部getter对象,根节点状态会作为第三个参数暴露出来。
1 | getters: { |
1 | <p>{{$store.getters.fullinfo}}</p> |
#####(4)模块内的actions
1 | actions: { |
打印结果:
当然,还有另外的一种es6的写法——对象的解构
3.命名空间
默认情况下,模块内部的 action、mutation 和 getter 是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一 mutation 或 action 作出响应。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。
1 | const store = new Vuex.Store({ |
更多详细内容可以参考官网
五、项目结构
以购物车为例

